A person pushes a car
The SI unit of force is
newton (N).
Newton
Is the amount of force which
will cause a mass of 1kg to move with an acceleration of 1m/s2.
Force = mass ×
acceleration, F=ma.
When
mass=1kg
Acceleration=1m/s²
F=1kg×1m/s² =1N.
What force can do?
ü Can
cause the object to move
ü Can
cause object to stop
ü Can cause the change of shape and size of an
object
ü Can
cause the change of direction of an object
TYPES
OF FORCES
1.
Fundamental forces
2.
Non fundamental force
The force can be action in contact force or action at distance force.
ACTION IN CONTACT
In action in contact there
is physical contact between the force and the point of application of force.
Examples of action in contact forces are driving a nail into a wood by hammer
(impact), kicking the ball, Tension force, elastic force, friction force and
air resistance.
ACTION AT DISTANCE
FORCE
In action at
distance there is no physical contact between the force and the point of
application of a force and yet a force can cause effect on the point of
application i.e. it can pull or push
object. Examples of action at distance forces are gravitational force and
electromagnetic force.
FUNDAMENTAL
FORCES
There are four
fundamental forces; these are called fundamental forces because they are the
basic forces occur in nature.
I.
Gravitational
force
II.
Electric
force
III.
Strong
nuclear force
IV.
Weak
nuclear force
GRAVITATIONAL
FORCE
This force is
equal to the weight of an object; the earth and other planet pull the objects
towards themselves by the force of gravity. To find the weight of an object we
find the force an object exerts on anything which is freely supporting it.
Since the weight
is equal to gravitational force it is common to refer gravitational force of
the earth on an object as the weight of an object so it is also obvious to say
weight of an object is the force of attraction of the earth on an object towards its
center.
In fact the
earth pulls the object by its gravity and in turn the object exerts a force on
something which supports it and the force is what is referred as weight.
Value of
gravitational field strength on the earth
Gravitational
field strength is a force per unit mass on an object, on earth the gravitation
field strength is 9.8N per kilogram (9.8N/Kg). This is also called acceleration
due to gravity or acceleration of the free fall and it is given as 9.8m/s².
1kg = 9.8N
Mass ? =F
By
crossing multiplication of the above, the relation will be
F=Mass×9.8,
since 9.8 is symbolized by ‘g’ and mass by m then F=mg.
From
F=mass × acceleration (F=ma)
Then
g=a. therefore gravitational field strength can be expressed as force per unit
mass or as acceleration.
Properties of gravitational force
ü
It
is always attractive (always pulling objects and never repels)
ü
It
is the weakest force compared to other fundamental forces
ü
It
is central force( it acts between center of masses
ü
It
operates over long distance.
ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE
This
is both magnetic and electric, it stronger than gravitation force. Example
of the electromagnetic forces
is
I.
Force
in formation of molecule of a substance, Atoms attracts each
other by the electromagnetic forces and combine to form molecule.
Example hydrogen
atoms combine with oxygen to form a molecule of
Water.
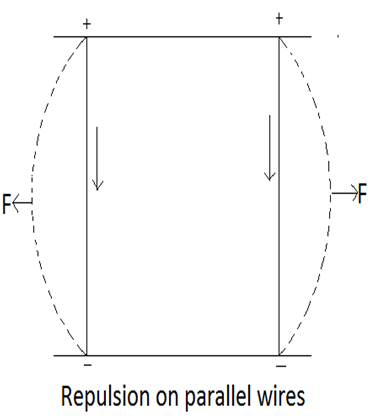
II.
Force
existing between two parallel wires carrying current placed a certain distance
apart.
I.
Force
between two charged particles.
Properties
of electromagnetic force are
ü
It
can be attractive or repulsive
ü
It
is stronger than the force of gravity
ü
It
is central force
ü
It
operates over long distance.
STRONG
NUCLEAR FORCE
Is
the force which binds together the proton and the neutron in atomic nucleus.
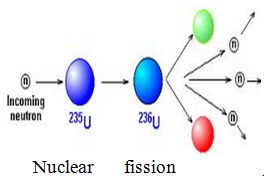
Energy
is released in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission is the reaction
in which an atomic nucleus of a radioactive element splits by bombardment from
an external source and nuclear fusion is the fusing together of lighter atomic
nuclei to form heavier one.
Both
processes release strong nuclear energy.
Nuclear fusion
Properties
of strong nuclear force.
ü It is an
attractive force
ü It is operates
in very short distance.
ü Non central force, it acts within the atomic
nucleus.
ü It is stronger
than gravitation force.
WEAK
NUCLEAR FORCE
Is
the force which occurs in some nuclear processes example radioactive decay and nuclear fusion of subatomic particles
Radioactive
material emits gamma ray, beta particle and alpha particle
Properties of weak nuclear force.
ü
It
is stronger than gravitational force but weaker than electromagnetic force
ü
It
is act in very short distances.
ü
It
is weaker than strong nuclear force
EFFECTS
OF FORCES
ü
Stretching
This is the
increase in length of an object when a force is applied, example pulling a
rubber band or spiral spring, the force responsible for this change is called stretching
force
stretching a spiral spring
ü
Compression
This is decrease
in volume or size of an object when a force is applied on it. Example squeezing
a spongy, compressing a gas in piston, and compressing a spiral spring. The
force which cause compression is called compressional force
Compressing a spiral spring
ü
Restoring
Elastic
materials when are stretched, compressed or twisted can return into their
original shape and size when the force is removed, this is called restoring.
The force which cause material to retain its original shape and size is called restoring
force
Spring
has returned to its original shape after stretching or compression force
removed
ü
Torsion
This is twisting
of object by
applying a force to one end while the other is held firm or twisted in the
opposite direction. The force which causes twisting is called torsional
force
Twisting a ruler
ü
Attraction
Attraction is a
pull without physical contact example of attraction is gravitation attraction,
attraction on unlike charged particles and magnetic attraction. The force which
cause objects to be attracted is called attraction force
ü
Repulsion
A force that tends to push two objects further
apart, example force on like electric charges or like magnetic poles.
The force
responsible for repulsion is called repulsion force
Repulsion on like charged
particles
ü
Friction
This is
opposition to motion, the force which opposes motion is called friction
force, it occurs between two surfaces moving relative to one another.
Advantages
of friction force
ü
It
enables us to walk
ü
It
enables objects to stop.eg car,bycicle
and motor bike
ü
It
enables us to start fire
Disadvantages
of friction force
ü
It
causes wear and tear of machinery parts
ü
It
produces undesired heat on machinery parts
ü
It
produces noise
QUESTIONS
1.
Define
the term force.
2.
What
are types of force
3.
Name
the four basic interactions of nature.
4.
Illustrate
any two effects of force you know.
5.
Give
two examples of action at distance force
6.
Is
compressional force action in contact force?
7.
List
five advantages of friction force










This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThe notes is really not expressed in detail but it has some facts
ReplyDelete